Financial Accounting / Chapter 1
Introduction to Financial Accounting

Overview
Accounting - the language of business, is the process of sharing, measuring & processing any business entity’s financial information. The information is presented in a particular format and used by several stakeholders for decision-making.
It further has 3 branches under it:
- Usually financial in nature
- Presented in a particular format
- Used by several stakeholders for decision making
Scope: To understand the basics of accounting
- What is Accounting?
- Different branches of Accounting
- How accounting helps in the decision-making process?
This accounting information is used differently by different stakeholders to make crucial decisions regarding the evaluation of assets, estimation of risk involved, and calculation of the profitability of important investment decisions.
Accounting
Accounting is the process of measuring, recording, summarising & communicating the financial transactions of any business entity. The information is usually presented in a particular format and used by several stakeholders for decision-making, cost planning & measurement of economic performance.
All business entities, irrespective of their sizes, maintain an accounting system. However, it looks different for each of them.

For instance, a typical manufacturing unit maintains an accounting system with the following information to determine the cost of manufacturing one unit of the product
- 3 types of inventories (raw, in-process, finished products)
- Number of utilised labour hours
- Other allocated expenses

Whereas, a retailer’s needs are very different Retailers mostly sell on a cash basis, hence, they also need information regarding bank accounts, credit card processing fees & time. An accounting system for a retailer would entail details about the inventory like
- level of inventory
- Inventory turnover rate
- Reorder points
- Accounts payable
Branches of Accounting
3 main branches of accounting originated considering the purpose & kind of information required by different stakeholders of a business.

Financial Accounting
Financial Accounting is often used interchangeably with accounting since both are used to prepare business’ books & records to generate financial reports.
It can be defined as the art of recording, classifying, summarizing & interpreting the results of transactions and events in a significant manner & terms of money.
The financial accounting information is summarised in the financial statements which are presented in the annual reports of the business entities. This information also summarises the past performance of the entities, since past performance is one of the key determinants for predicting future performance.
Financial accounting answers the 2 most relevant questions:
- Q1. How did the business perform in terms of profit & loss during a particular period, called an accounting period ?
- Q2. What is the financial position of the business at a point of time?
These questions are answered by the 2 major financial statements - income statement & balance sheet
- The income statement shows the business performance in terms of profit or loss during an accounting period.
- The balance sheet depicts the financial position of the business at the end of the accounting period.

Cost Accounting
Cost Accounting is a formal system of maintaining the books of account to ascertain, control & reduce the costs of products & services. It is a systematic set of procedures to report & analyse a company’s cost structure.
Often, costing & cost accounting is used interchangeably. However, there lies a major difference between the 2.
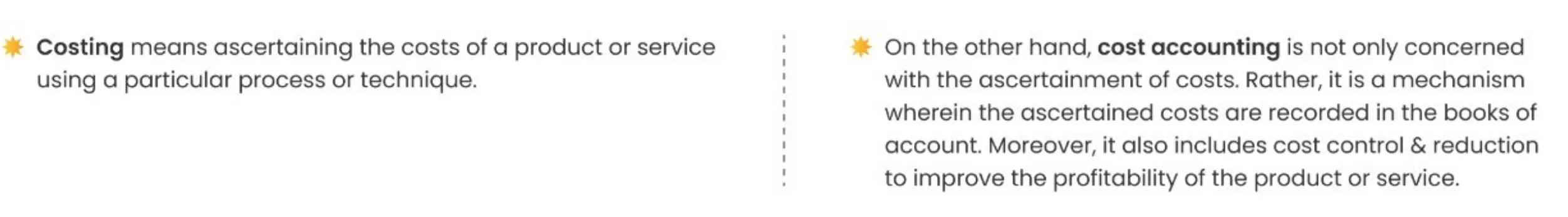

Management Accounting
Management Accounting is concerned with identifying, presenting & interpreting financial information for planning, controlling & decision-making. This system of accounting provides relevant information to managers for performing their functions & making strategic decisions effectively.
What is the difference between Financial Accounting, Cost Accounting & Management Accounting?
| Basis | Financial Accounting | Cost Accounting | Management Accounting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To present a true and fair view of the business’s income & financial position at regular intervals. | To determine, control, project & reduce the costs associated with a project or service to aid business decisions. | To make accounting information useful for management to make effective strategic decisions. |
| Kind of Information | Concerns with past information of the organisation | Concerns with past as well as pre- determined costs. | Concerns with decisions to be taken in the future after using past data for future projections. |
| Users | External stakeholders such as stakeholders, loan providers, government agencies, suppliers, etc. | Internal stakeholders such as managers, top executives, department heads, etc. | Internal stakeholders such as managers, top executives, department heads, etc. |
How accounting aids decision-making?
Accounting is used by several stakeholders to make different decisions. Let’s go through some examples to understand this better.
- Take lending decisions & check creditworthiness
XYZ textiles has applied to HDFC bank for a loan of 50 crores for business expansion. To examine whether a loan should be given, the bank will examine the past performance using its financial statements. They will also analyse the projections furnished by the company to know how it will be utilising the loan amount to generate more business. All of this is done to ensure the company meets their principal & interest obligations.
- Conduct a comparative analysis of financial statements
Conduct a comparative analysis of financial statements XYZ textiles has a competitor PQR manufacturers. Since they are in the same business line, both of them incur identical transactions throughout the year. Mr. B, an investor has to decide whether to invest in XYZ textiles or PQR Manufacturers for which he’ll conduct a comparative analysis of the financial statements of both companies.
- Downsizing your workforce
XYZ plans to cut down its costs and decides to lay-off the unproductive labour. The accountant produces reports on the productivity of each labour and relates it to their wages and other associated costs for labour maintenance and welfare. Based on these reports, the management decides whom to be laid-off.
- Future planning
XYZ currently deals with only garments for the age group of 0-12 years. However, in its expansion policy, it aims to manufacture garments for the 12-30 years of age group. The accountants at XYZ develop reports consisting of estimated sales, production & selling costs. The management will then decide whether to manufacture and sell the new age-group garment line or not.
Closing summary
To sum up, accounting assists in analysing and reporting the costs and benefits of each decision in quantifiable terms for effective decision making by the stakeholders. In the subsequent chapter, the key accounting terms, concepts, and principles will be discusses to explain how financial accounting works.
